Given the growing number of patients with prostatitis, the pharmaceutical industry offers hundreds of different drugs for this disease, and the arsenal of drugs is constantly replenished. Faced with this problem, most men do not go to the doctor, but to the pharmacy, hoping to get a "miracle cure" that will free them from these plagues in a few days. Without understanding the problem, a person does not understand which prostatitis pills are cheap andeffective for him. The pharmacist also can not answer this question, offering the most popular drugs that can prove completely useless and even harmful.
The specialist should choose an effective therapeutic regimen, taking into account the form and stage of disease development, the individual characteristics of the patient and the presence of contraindications. The drugs used are divided into the following groups:
- Etiotropic - antibacterial agents designed to destroy infectious pathogens.
- Symptomatic - relief of painful symptoms.
- Pathogenetic - contribute to the elimination of congestion in the pelvic area, improve the blood supply to the prostate.
Complex drug therapy includes the use of such drugs:
- Antibiotics.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- α-blockers.
- Antispasmodics.
- Means to improve blood circulation.
Consider in detail tablets for prostatitis in men.
Antibacterial agents
They represent a shock group in the composition of drug therapy, they are used in acute and chronic diseases. Their task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms, alleviate the symptoms of intoxication and reduce inflammation. Since each infectious agent is sensitive to certain antibiotics, bakposev is carried out to select the right drug.
Drugs for the treatment of prostatitis in men are available in the form of tablets, injections, in the form of rectal suppositories and solutions for instillation (injection of the drug into the urethra). Urologists are of the opinion that in inflammation of the prostate the most pronounced therapeutic effect is observed with rectal administration of the drug.
The antibiotics used are divided into the following groups:
- Fluoroquinolones - have the most pronounced therapeutic effect.
- Cephalosporins are effective against many pathogens, but they have a short effect.
- Aminopenicillins - are indicated for mild inflammation, without complications, rare exacerbations of chronic form.
- Tetracyclines - rarely cause side effects. Compared to other antibiotics, they show more pronounced activity against atypical pathogens (mycoplasmas, chlamydia).
- Macrolides - have a weak therapeutic effect, but at the same time have low toxicity.
The complex treatment regimen includes antibacterial drugs:
> zxtable border = "1" cellpadding = "0" >Anti-inflammatory drugs
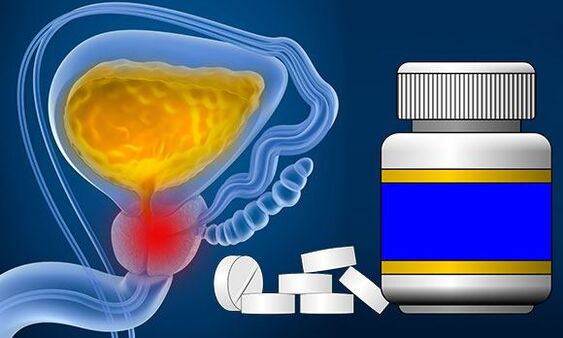
Anti-inflammatory drugs for prostatitis are used in combination with antibiotics. Nonsteroidal drugs help reduce glandular swelling, thus reducing urethral compression and difficulty urinating. Also, these drugs have an analgesic effect. If drugs of this group do not have a positive effect, the patient is prescribed strong hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Other means

One of the most unpleasant symptoms of prostatitis are problems with urination caused by spasms of the smooth muscles of the gland and urea. A group of α-blockers is used to eliminate this violation. Their action is aimed at relaxing muscle fibers and facilitating the release of urine.
Antispasmodics are prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Today, it is impossible to name the best cure for prostatitis, because each patient responds differently to drug therapy. Means that are effective in one case can be completely useless for another patient.
Inflammation of the prostate develops not only as a result of exposure to pathogenic pathogens, but also as a result of congestion. Such disorders also prevent rapid tissue regeneration, restore the functions of the affected organ, and reduce the therapeutic efficacy of drugs. To remove them, drugs are used to improve the blood supply to the gland.
Preventive measures
To maintain a healthy prostate you need:
- Proper nutrition - the diet should include foods that supply the body with the necessary macro- and microelements, vitamins.
- Regular intimate life.
- Timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Enough physical activity.